3D Printing
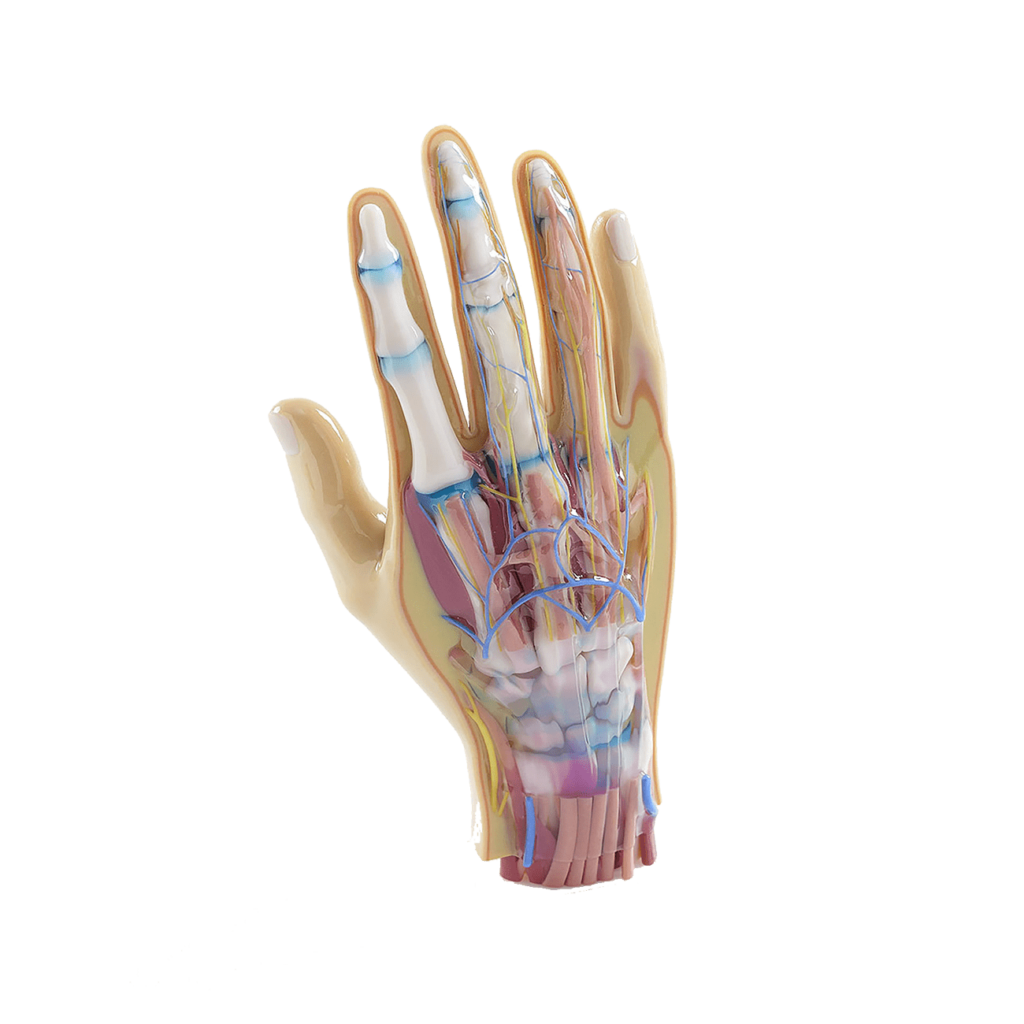
Preparing models for 3D printing based on medical data.
Printing of anatomical models using the full spectrum of printing technologies.
Expert support in data processing and model print execution.
3D Printing
Preparing models for 3D printing based on medical data.
Printing of anatomical models using the full spectrum of printing technologies.
Expert support in data processing and model print execution.
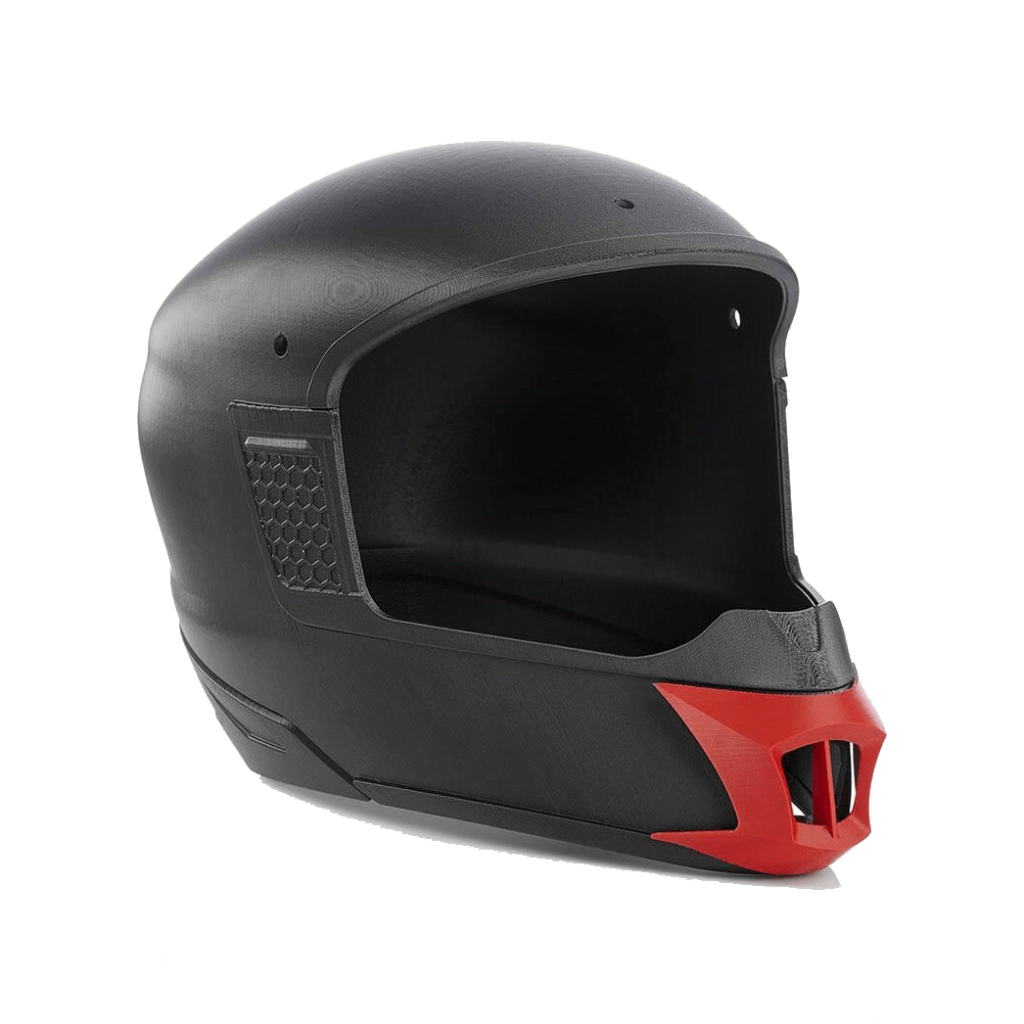

FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
Prototyping and spare parts
3D printing technology that involves the deposition of molten material. Developed in the 1980s, the method is now the most widely used 3D printing technology. The building material is a thermoplastic material in the form of monofilament wound on spools. During the printing process, the material is heated and melted in the head – extruder, and then distributed layer by layer according to the outline of the 3D model. The advantages of this method are the ease of manufacturing, high availability of materials and the possibility of obtaining low-budget prints. A characteristic feature of printouts is a clear layering visible on the surface of the object. This technology is recommended for rapid prototyping, printing spare parts for devices, tools, accessories, utility parts.
SLA (Stereolithography)
High precision and smooth printing
Technology using liquid photopolymer resins that are cured layer by layer with laser light. It is the oldest 3D printing method used in industry, medicine and dentistry. The biggest advantages of SLA technology are: high precision of manufacturing, exceptional smoothness of the surface, the possibility of obtaining organic shapes, a wide selection of materials (rigid, flexible, transparent, biocompatible). The method requires the use of support structures removed manually.
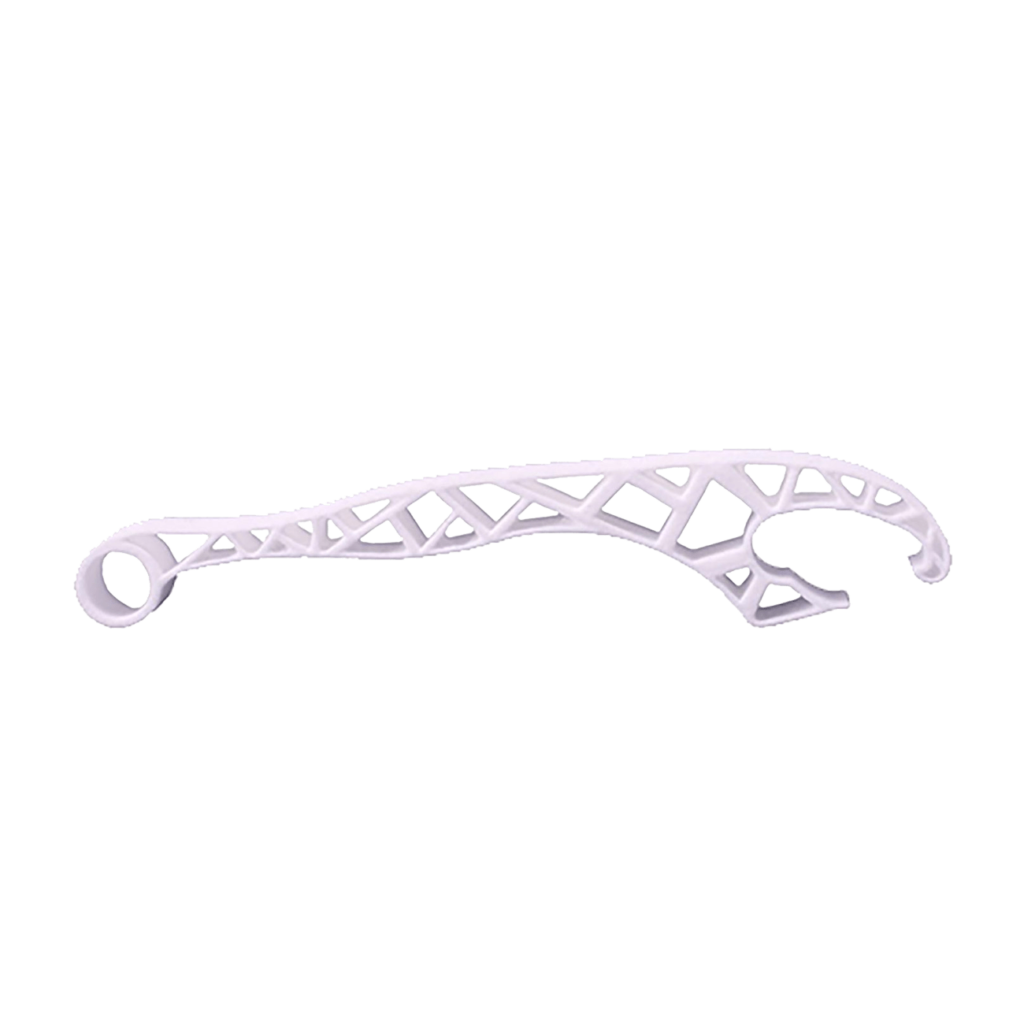


SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
High speed printing technology
A 3D printer working with SLS technology sinters powdered polyamide layer by layer using a focused laser beam. The biggest advantages of the SLS technology are: speed of printing, durable materials, and the possibility of obtaining very complex geometries and moving assemblies in a single printout due to the lack of support structures. Powdered materials are used for printing, hence the print surface has a characteristic porosity. This method is recommended for efficient serial production.
PolyJet
Multi-material and multi-color printing
The technology developed by Stratasys is the most advanced method of 3D printing from synthetic materials. The building material is liquid photopolymer resins, which are sprayed onto the work table layer by layer and then cured with UV light. With PolyJet 3D printers, we can make multi-color and multi-material prints in a single process. Thanks to the use of easily removable support material we can obtain very complicated geometries and small details. A printout made with the PolyJet technology has a smooth surface without any noticeable layers.
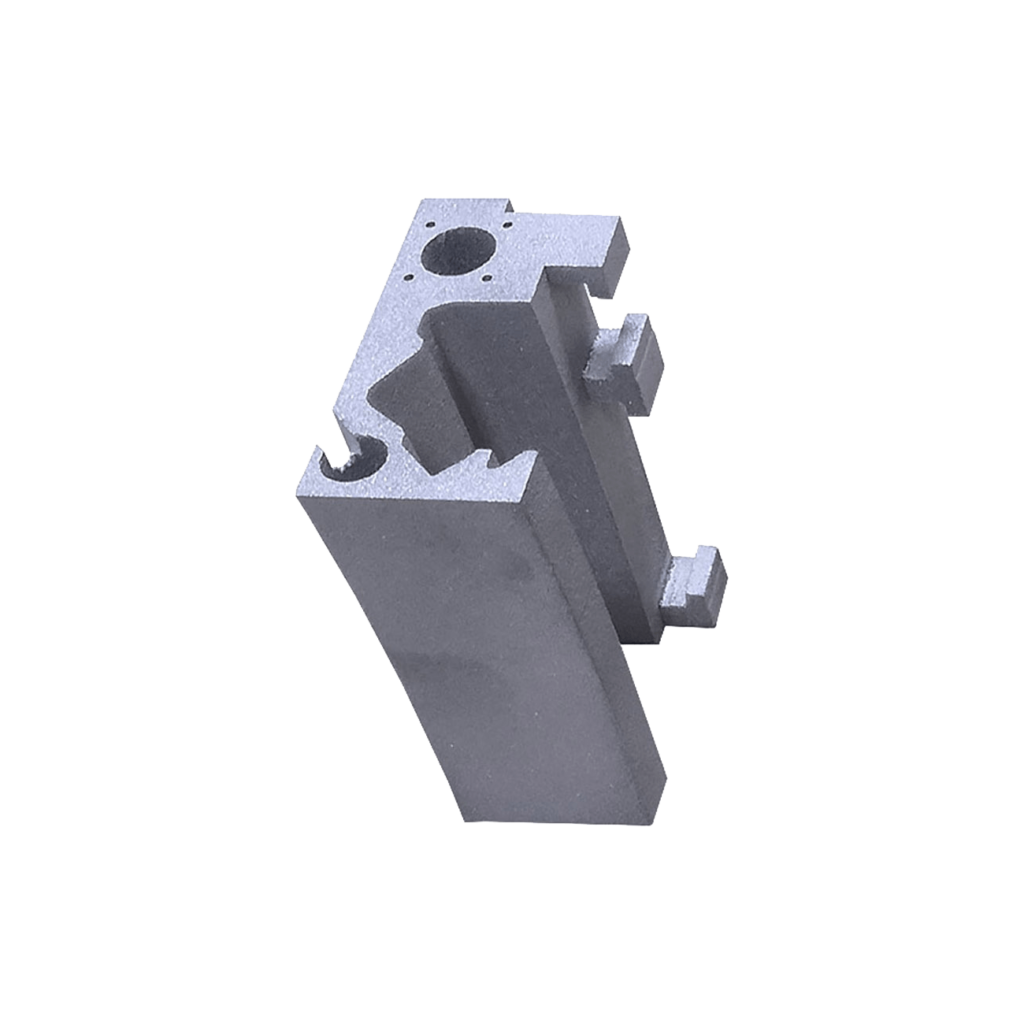

DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering)
High print durability
For 3D printing, this technology uses powdered metal alloys (usually aluminum alloy and titanium alloy). The principle of operation is similar to SLS technology, but the laser completely melts the powdered material, instead of just sintering it. The components obtained in this way are characterized by high strength and possibility of further processing. They can be used as finished parts in many sectors of industry and medicine.
Send a request
Discuss the model with your engineer
Get the final product